Each time you click a switch, electricity flows to a light fixture and turns on instantly. Ever wondered how the electricity gets there? What happens behind the shady business of bringing light to your personal space is a dazzling domain of science, machines, and workers brought together inside power plants. These facilities – at work 24/7 – serve as the foundation of the modern world, providing light, energy, and power to our homes, schools, hospitals, manufacturing, and more.
What is a Power Plant?
A power plant is a large facility used to convert energy into electricity. There are different forms of power plants and types of energy sources, including coal, natural gas, water, wind and sunlight, but ultimately they have the same purpose: to generate electricity in a safe and reliable manner.
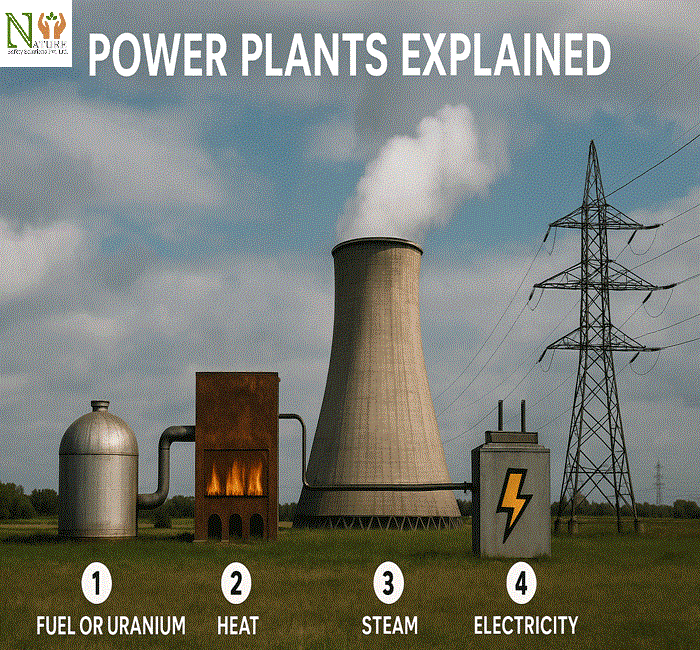
Many power plants used some type of energy from a fuel source to heat water, producing steam. The steam turning a turbine consumes sufficient motion to move a generator that converts the motion into energy, sending electricity down power lines to our televisons, refrigerators, medical devices, and power tools.
Categories of Power Generating Facilities
1. Thermal Power Facilities
Thermal power plants generate heat by combusting natural gas, coal, or oil. The heat converts water into steam, which is used to drive a turbine. Thermal power plants are widely used but produce emissions which is leading to the exploration of cleaner alternatives.
2. Hydroelectric Power Generating Facilities
Hydroelectric power generating facilities use the force of moving water. Dams are used to store water in canals or reservoirs, and then the water can be released and passed through turbines to generate the power converted from kinetic energy to electricity. Hydroelectric power is renewable, and does not create air emissions.
3. Solar Power Generating Facilities
Solar power generating facilities use solar light as an energy source. Solar panels collect solar light and then convert to electricity using photovoltaic cells. These facilities are best located in parts of the world that are sunny. Solar power facilities are becoming much more popular as they are clean energy and sustainable.
4. Wind Power Generating Facilities
Wind power generating facilities gather the forces of moving air to create electricity. When wind travels and makes the blades spin, it creates the power. Wind farms are outlined in wide open fields, as well as offshore wind generating facilities.
5. Nuclear Power Generating Facilities
Nuclear power generating facilities use uranium fuel rods in order to create heat in a controlled manner. Creating an internal heat creates steam that turns turbines as well. Nuclear energy is efficient and can create a tremendous amount of power, as well as has low emissions. Nuclear Generating Facilities must follow regulations and protocols of safety, as well as take care of disposal of waste in a careful manner.
How Electricity Moves Around
When electricity is generated, it doesn’t simply stay within the power generation facility. Instead, it is sent across a lengthy and intricate series of networks known as the power grid. While the electricity is sent through high voltage transmission lines over long distances, it then travels into substations where the voltage is lowered to allow it to go safely into homes and businesses.
This process is instantaneous – it’s so quick that the electricity you are using right now was likely generated only minutes ago.
Who Makes It Happen
Power generation plants have engineers and professional employees watching over every electro-mechanical process. Engineers are checking the machines used for generation to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Technicians inspect and maintain turbines, boilers, safety systems, and equipment. Control room operators manage the electricity supply to the grid, ensuring a proper balance of supply and demand at all times.
Without these crucial professionals working tirelessly, you wouldn’t enjoy modern conveniences such as air conditioning, computers, and street lights.
The Call for Energy that is Cleaner
Conventional power-producing facilities, especially fossil fuel power plants, are environmentally damaging. They emit greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. This is why countries are investing in renewable resources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric.
These days, contemporary power plants are equipped with advanced technologies that minimize emissions, recycle water, and improve fuel efficiency. Hybrid plants even combine solar power with thermal systems to have the advantage of both.
Importance of Power Plants
Power plants are not just big buildings with machines in them — they are lifelines for our cities. They ensure every factory operates, every train moves, and every home stays warm in winter.
Technology supports power-producing structures in changing from traditional plants to modern power plants. Gall stage power plants will be cleaner, smarter, and more efficient. Power plants are helping to stimulate a sustainable future while keeping our present illuminated.
Also read:-
